
What is Rheumatoid Factor?
Discover more about the role of rheumatoid factor in rheumatoid arthritis
What is Rheumatoid Factor?
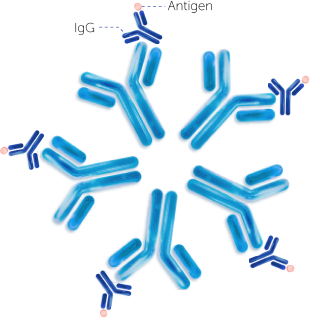
In rheumatoid arthritis, rheumatoid factors are mainly of IgM, IgG and IgA isotypes, but IgE and IgD have also been reported.1,3–5 IgG-reactive B-cells produce rheumatoid factors with high antigen-binding affinity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.6
These rheumatoid factors can bind to the IgG’s Fc region.1,6
This interaction leads to the formation of large immune complexes.4,6,7 These immune complexes are internalised by macrophages through the Fc-gamma receptor (FcɣR) and are degraded by the lysosome.4,8
RF Immune Complex
Immune Complexes are Degraded by Macrophages
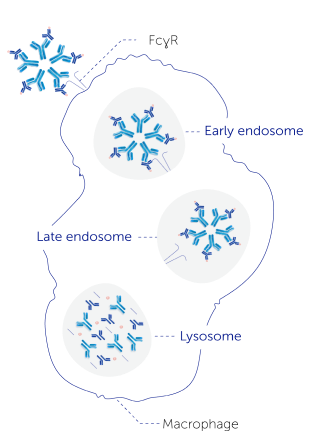
Testing for rheumatoid factor is easily accessible in the clinic and can be used to support a diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis,3,5 a chronic inflammatory joint disease which leads to various other symptoms and extra-articular organ manifestations.12,13
Rheumatoid factor seropositivity is different from high rheumatoid levels. No established guidelines define what are high rheumatoid factor levels and different trials use different cut-off values defining high rheumatoid factor levels.10,11,14–17
Around one in four patients with rheumatoid arthritis have high rheumatoid factor levels of above 200 IU/ml.15–17
Patients with rheumatoid arthritis and high rheumatoid factor levels are more inclined to experience:

Worse outcomes18-21
Higher disease activity21
Low rates of remission21
More aggressive disease and higher risk of radiographic progression21–23
Higher prevalence of extra-articular manifestations,22,24 associated with unfavourable outcomes for joint destruction and disability25
Increased risk of cardiovascular
disease-related mortality26
EU-DA-2300317
Date of preparation: August 2024